Permissions
Permissions in HumHub are used to grant users access to specific areas or functions of your network.
Use Cases
- Group A needs permission to manage the users of the network.
- Moderators of Space A need write permissions for Module X.
- User A only allows friend users to send him messages.
To achieve the permission management in such cases, HumHub provides an own group and contentcontainer level permission system.
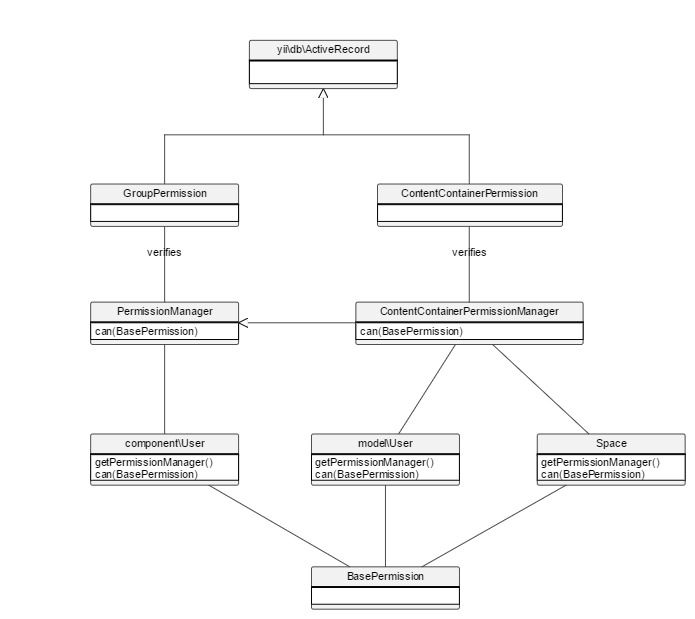
There are two different types of permission: humhub\modules\user\models\GroupPermission and humhub\modules\content\models\ContentContainerPermission.
Verifying permissions
Permissions are verified by means of a humhub\modules\user\components\PermissionManager.
There are two types of humhub\modules\user\components\PermissionManager|PermissionManager, one for verifying humhub\modules\user\models\GroupPermission|GroupPermissions
and one for humhub\modules\content\models\ContentContainerPermission|ContentContainerPermissions.
Group Permissions
humhub\modules\user\models\GroupPermission|GroupPermissions are system wide permissions which can be assigned to system groups (Administration -> Users -> Groups).
Example of GroupPermissions `GroupPermissions are
humhub\modules\admin\permissions\ManageUsers- Permission to access the global user management section.humhub\modules\admin\permissions\ManageGroups- Permission to access the global user group section.humhub\modules\space\permissions\CreatePublicSpace- Permission to create public spaces.
Verify Group Permissions
Group permissions of the current user can be verified by calling humhub\modules\user\components\User::can():
// Note that we are using the user component and not the user model here!
Yii::$app->user->can(MyPermission::class);
// or
Yii::$app->user->permissionManager->can(MyPermission::class);
// or manually
// Note that you can leave the subject parameter if you want to verify against the currently logged in user model.
$permissionManager = new PermissionManager(['subject' => $myUserModel]);
$permissionManager->can(new MyPermission());
Content Container Permissions
humhub\modules\content\models\ContentContainerPermission|ContentContainerPermissions are container (Space/User) specific permissions and can be assigned to
so-called user-groups.
User user-groups:
User::USERGROUP_SELF: The permission container is the user instance itself.User::USERGROUP_FRIEND: The permission container is a friend of the user.User::USERGROUP_USER: The user is just a network member, but does not have any specific relationship with the permission container.User::USERGROUP_GUEST: The user is a guest user and therefore has no relationship with the permission container.
Space user-groups:
Space::USERGROUP_OWNER: User is the owner of the space.Space::USERGROUP_ADMIN: User is member of the space administrator group.Space::USERGROUP_MODERATOR: User is member of the space moderator group.Space::USERGROUP_MEMBER: User is a simple member of the space.Space::USERGROUP_USER: User is not a member of the space but a member of the network.Space::USERGROUP_GUEST: User is not a member of the space nor a member of the network.
Example of ContentContainerPermissions are:
humhub\modules\space\permissions\InviteUsers- Permission to invite users to a space.humhub\modules\mail\permissions\SendMail- Allows/Disallows other users to send messages. (Require to install Mail module)humhub\modules\content\permissions\ManageContent- Permission to archive, pin to top or delete content within a space.
Verify ContentContainer Permissions
// check if the current user is allowed to send messages to user A
$userA->can(SendMail::class);
// check if the current user is allowed to manage content in spaceA
$spaceA->can(ManageContent::class);
// or
// Note the 'all' parameter is used in this example to require all given Permissions to be verified successfully instead of only one.
$permissionManager = new ContentContainerPermissionManager(['subject' => $myUserModel, 'contentContainer' => '$mySpace']);
$permissionManager->can([new MyPermissionA, new MyPermissionB], ['all' => true]);
Custom Permissions
All permission classes are derived from humhub\libs\BasePermission and should reside in the permissions directory of your module.
A humhub\libs\BasePermission subclass should at least overwrite the following attributes:
humhub\libs\BasePermission::id|BasePermission::id- A unique permission id.humhub\libs\BasePermission::moduleId|BasePermission::moduleId- The moduleId this Permission belongs to.humhub\libs\BasePermission::title|BasePermission::title- Permission title used to display the permission.humhub\libs\BasePermission::description|BasePermission::description- Short description of the permission.
Default State
By default a permission is only granted if either the humhub\libs\BasePermission::$defaultState|BasePermission::defaultState is set to humhub\libs\BasePermission::STATE_ALLOW|BasePermission::STATE_ALLOW
or if the given group is contained in the humhub\libs\BasePermission::defaultAllowedGroups|BasePermission::defaultAllowedGroups array.
The default state of a group can either be overwritten by setting a group state in the database
// This is normally handled by the permission settings grid.
$user->getPermissionManager()->setGroupState(User::USERGROUP_USER, new SendMail(), BasePermission::STATE_ALLOW);
or by overwriting the default behaviour
return [
...
'params' => [
// Grant SendMail permission for group User::USERGROUP_FRIEND
'defaultPermissions' => [
'humhub\modules\mail\permissions\SendMail' => [
'u_friend' => 1
]
]
],
...
];
Fixed Groups
The default-state of a group can be fixated by overwriting the humhub\libs\BasePermission::fixedGroups|BasePermission::fixedGroups array within your permission class.
This will disable the edit capabilities of the given groups.
By default the following space user-groups are fixed:
Space::USERGROUP_GUESTSpace::USERGROUP_OWNERSpace::USERGROUP_ADMIN
Edit Permissions
If you plan to make your custom permissions editable, you have to return an array of all your module permissions within the
humhub\components\Module::getPermissions()|Module::getPermissions() method of your Module.php. Your permissions will be added automatically to
the permission grid of your content-container or to the global permission settings in case of group level permissions.
public function getPermissions($contentContainer = null)
{
if ($contentContainer instanceof Space) {
return [
new permissions\MySpacePermission()
];
} elseif ($contentContainer instanceof User) {
// This module does not provide yn user level permission
return [];
}
return [
new permissions\MyGroupPermission()
];
}
Controller Access Permission
To restrict the access to a controller or specific controller actions your controller should overwrite the
humhub\components\Controller::getAccessRules() function. This function should return an array of access rules as:
class SpecialController extends Controller
{
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
// This will block all controller actions for non loggedIn users.
['login'],
// This will block the secret action for users without SpecialPermission
['permission' => [SpecialPermission::class, 'actions' => ['secret']]
]
}
public function actionIndex()
{
// Only accessible by logged in users
}
// Will only be allowed for users with SpecialPermission
public function actionSecret()
{
// Only accessible by users with SpecialPermission permission
}
}
The set of available rules is defined by the humhub\components\access\ControllerAccess which is defined by
humhub\components\Controller::access. There are three ControllerAccess classes available:
humhub\components\access\ControllerAccess- default access controlhumhub\components\access\StrictAccess- adds an additional restriction for guest users in non guest mode environmentshumhub\modules\content\components\ContentContainerControllerAccess- default access control inContentContainerController
In the following, we'll show some more use cases for the getAccessRules function:
Disable guest access for all controller actions:
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
['login']
];
}
Disable guest access for specific controller actions:
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
['login' => ['action1', 'action2']]
];
}
All users have to be logged in + additional permission check for 'action1' and 'action2':
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
['login'],
['permission' => MyPermission::class, 'actions' => ['action1', 'action2']]
];
}
Custom inline validator for action 'action1':
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
['validateMyCustomRule', 'someParameter' => 'someValue', 'actions' => ['action1']]
];
}
public function validateMyCustomRule($rule, $access)
{
if($rule['someParameter'] !== 'someValue') {
$access->code = 401;
$access->reason = 'Not authorized!';
return false;
}
return true;
}
ContentContainerControllerAccess
The ContentContainerControllerAccess used in ContentContainerController provides some additional access rules as:
ContentContainerControllerAccess::RULE_SPACE_ONLYrestrict to space requestsContentContainerControllerAccess::RULE_PROFILE_ONLYrestrict to user account requestsContentContainerControllerAccess::RULE_USER_GROUP_ONLYrestricts the access to a given level of container groups
The following example restricts the access for non members of a space. Note the USERGROUP_MEMBER should specify the minimum user group level which should be able to access the controller/actions.
public function getAccessRules()
{
return [
[ContentContainerControllerAccess::RULE_USER_GROUP_ONLY => [Space::USERGROUP_MEMBER]]
];
}
Guest Access
Since HumHub can also be operated in guest mode, you have to consider that a call to Yii::$app->user->getIdentity() may return a null value.
Therefore you should either block guest access in your controllers (see Controller Access) or add a check for
Yii::$app->user->isGuest before accessing your user identity.
See the User Section for more information and examples about how to use the user component.
Note: Global controllers (non ContentContainerController) should be protected by
StrictAccess
Note: Remember to hide view components as buttons and menus which are not accessible by guest users.
Note: If the guest mode is active, guest users are allowed to access public content.